If you are a digital marketer or own a website, you’re no stranger to the power of analytics. Universal Analytics is the big player that comes to mind when tracking user behavior and understanding how your website is performing. Oh, wait! The big player that comes to mind WAS Universal Analytics. Google gave its place to Google Analytics 4, the latest analytics properties by Google.

What upgraded properties of Google Analytics 4 make it better than Universal Analytics, a tool used by most Advertisers to date? Google reinforced the upgrade and gave a notice to migrate to Google Analytics 4 a year ago. Despite this, most advertisers are using Universal Analytics to date.
Let’s understand the key difference between GA4 and Universal Analytics and how to get started with Google Analytics 4 before Universal Analytics stops processing data.
Key differences: GA4 vs Universal Analytics!
Google Analytics Universal vs GA4 (Google Analytics 4). Both are like our trusty navigators on the seas of data, but they do have their differences. We’ll take you through the key differences between Universal Analytics and GA4 function by function. Let’s dive in!
Read:- Why You Should Upgrade to GA4 before Google Universal Analytics Sunset?
Users
Universal Analytics:
Universal Analytics tracks users based on unique cookies. It has two user metrics:
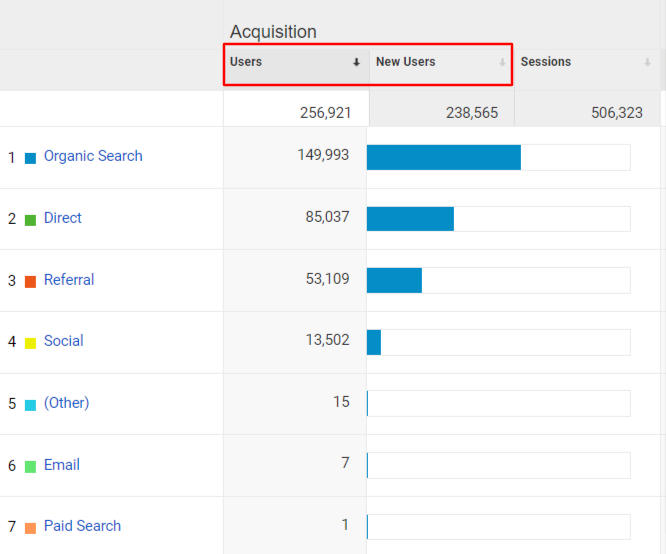
- Total users – Total no. of users, and
- New Users – The number of new visitors who visited your website for the first time. A new user is created each time a user visits your website from a new device or browser.
Google Analytics 4:
GA4 is a step ahead of Universal Analytics. It uses an event-based model, which means every interaction on your site is considered an event. Google Analytics 4 has three user metrics:
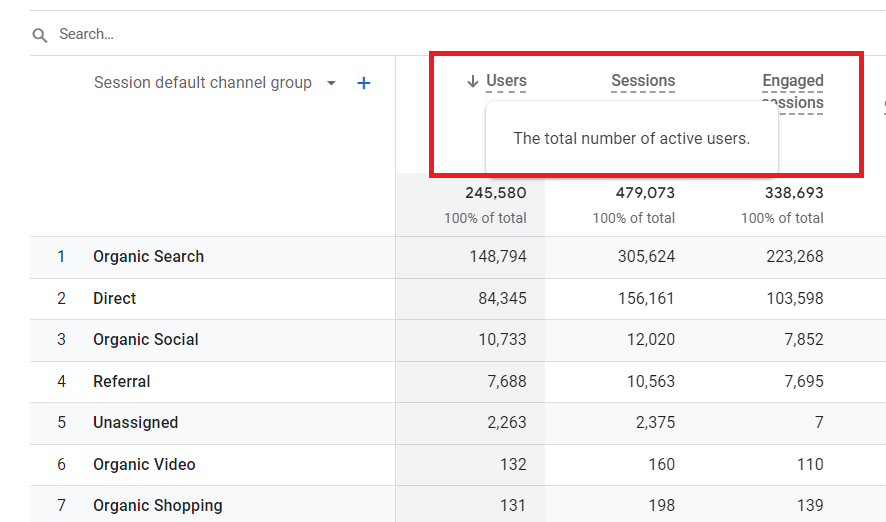
- Total Users – The total number of unique users that logged an event;
- New Users – The number of new users who interacted with your website for the first time. However, in this case, it is assessed by the number of new unique user IDs that logged the event, and
- Active Users – Users who are actively using the website.
In Google Analytics 4, multiple visits from the same IP address account for only one user. It offers a real and more holistic view of user engagement, even if they switch devices like a pro.
Pageviews
Universal Analytics: A pageview is recorded each time a page is loaded or reloaded, including repeated views of a single page.
Google Analytics 4: GA4, however, has a smarter approach. It tracks screen views, which include not just web pages but also app screens. It is particularly handy if you’ve got both a website and an app. Views of a single screen or page that are repeated are also counted.
Purchases
Universal Analytics: Universal Analytics provides a simple way to track ecommerce transactions. When you opt to send a purchase event, data is retrieved from a products array using Google Analytics-provided JavaScript and collected in a buy event.
Google Analytics 4: GA4 takes it up a notch. It uses enhanced measurement to automatically track and measure ecommerce events, making it easier to analyze your sales funnel and understand where your revenue is coming from. When collecting a purchase event, it does not provide any more JavaScript for array collection and expects you to provide the items array on your own.
Sessions
Universal Analytics: Universal Analytics defines a session as a sequence of user interactions on your site that occur during a 30-minute interval.
Google Analytics 4: In GA4, it’s more flexible. A session can span up to two hours of inactivity, accommodating how users engage with content today, which can involve longer browsing periods.
Session/Traffic-based Acquisition Metrics
Universal Analytics: Universal Analytics relies heavily on cookies to attribute traffic sources.
Google Analytics 4: GA4 uses a combination of first-party cookies, Google signals, and modeling to give you a better grasp of user acquisition. It helps fill in the gaps when cookies crumble under pressure.
Conversions
Universal Analytics: We’re all chasing conversions, right? Universal Analytics allows you to set up goals like digital high-fives for your accomplishments.
Google Analytics 4: GA4, on the other hand, introduces events as the building blocks for conversions. You have the freedom to customize these events according to your specific goals, making tracking more personalized and insightful.
Bounce Rate
Universal Analytics: Bounce rate – the ultimate “Oops, wrong party” moment for users. Universal Analytics considers a bounce as a single-page session.
Google Analytics 4: GA4, however, takes a closer look. It differentiates between engaged bounces (where users interact with your site content) and unengaged bounces (when they quickly bounce back).
Event Count
Universal Analytics: Events are the heartbeats of user interaction. In Universal Analytics, you have to set up events manually, which can sometimes be tedious.
Google Analytics 4: GA4, thankfully, automates event tracking by capturing interactions by default. It saves you time and ensures you’re not missing important data points.
Get started with Google Analytics 4!
It’s time that you get started with Google Analytics 4 if you haven’t already. Here are a few ways to help you get started.
Option 1
Configure Analytics data gathering. (if you’re new to Google Analytics and want to start collecting data for your application or website.)
Set up Analytics data collection if you’re new to Analytics and ready for data collection for your website or mobile application.
Step 1: Create an Analytics account if you don’t have one already.
Step 2: Create a new property with Google Analytics 4.
Step 3: Add a data stream
Step 4: Set up data collection property for websites.
Complete additional configurations and get more useful data out of Analytics after you have set up data collection.
Option 2
Option 2 is to add Google Analytics 4 to a website with Universal Analytics (Analytics “classic”).
Step 1: Create a GA4 property. Follow the following steps!
- Click Admin in Google Analytics.
- Ensure that you select your desired account in the Account column.
- Select the Universal Analytics property that collects data for your website and click GA4 Setup Assistant in the Property column.
- Choose how you wish your Universal Analytics property to be migrated.
- Depending on how your site is tagged, you’ll see one of the following options on the page:
- Choose “Create and continue” to continue Setting up a Google tag page.
- Create property. Analytics can reuse your Universal Analytics tagging for GA4 property.
- Manually install the Google tag or select which option best describes your situation.
Finish creating your new GA4 property. Continue and follow the instructions on the Set Up a Google tag page.
Step 2: Finish setting up your new GA4 property.
Option 3
Add Google Analytics 4 to a Content Management System (CMS) or a website builder platform.
It’s a great option for a Content Management System (CMS) hosted website. For instance, websites created with WordPress, Wix, Squarespace, Drupal, WooCommerce, GoDaddy, Magento, Shopify, HubSpot, Awesome Motive, and more.
Conclusion
And there you have it, folks! The key difference between Google Analytics GA4 and Universal Analytics. While Universal Analytics has been a trusty companion on our digital journeys, getting ready to adapt to GA4 is like the upgraded version with cool new features and a more adaptable mindset.
It’s time to set sail with the exciting possibilities of GA4, keep your data compass handy, and navigate your way to insights that will steer your online presence toward success.