In the intricate web of digital marketing and search engine optimization (SEO), terms like “crawlability” and “indexability” might sound intimidating at first. However, they are not difficult to understand and implement but are essential to understanding how search engines navigate and rank websites.
Imagine this: There’s a big library with millions of books. Among them is one book you wrote. It’s a great read and can potentially change people’s lives. The challenge is how readers would find it. Replace “library” with “internet” and “book” with “webpage.” In the internet’s case, the answer is Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Improving the webpage’s crawlability and indexability makes it simpler for search engines to discover and show the page to searchers.
In this blog, we will understand what is crawlability and indexability, how they impact SEO, and what steps you can take to optimize your web pages.
What is Crawlability?
Crawlability is the search engine’s ability to explore and analyze a website’s content. Search engines send bots, known as crawlers, to scan web pages. These crawlers read the website’s code, internal and external links, meta content, alt texts, and other elements to understand the page’s structure.
SEO intends to make the crawlability of the website simpler for search engines such as Google. It is vital for SEO because if the search engine crawlers can’t find and understand your website’s content, it won’t appear in the search results.
What is Google indexing in SEO?
Once the Google or search engine bots are done crawling your website, the next step is indexability. Indexability involves adding the crawled pages to the search engine’s index, a massive database of web pages. This index serves as a reference for search engines when users enter queries. It’s like the index at the back of a book that helps you find the pages containing specific information.
For a page to be indexable, it needs to have unique and valuable content. Search engines prefer original content that provides information, solves problems, or offers entertainment to users. Duplicate, low-quality, or irrelevant content is often ignored during indexation.
Key Factors Affecting Crawlability and Indexability
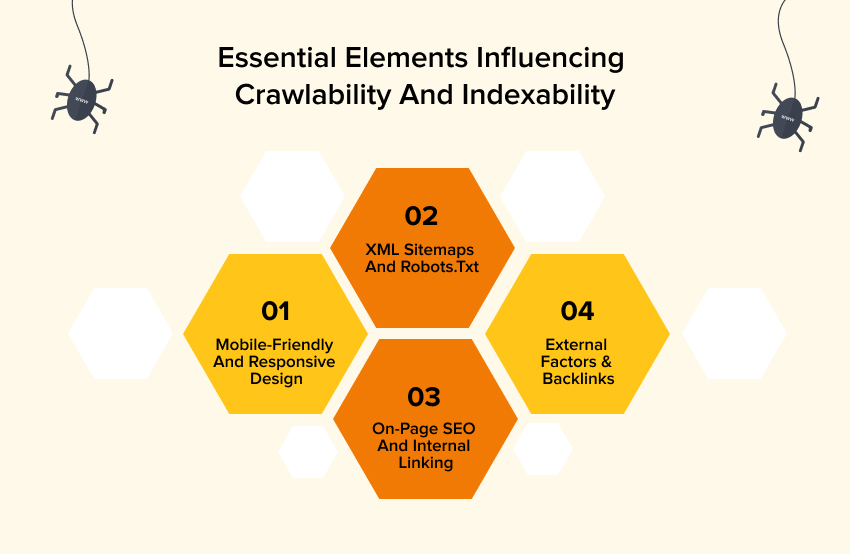
Several factors influence how well search engines can crawl and index your website.
- Mobile-Friendly and Responsive Design: Mobile-friendliness has become crucial since Google started prioritizing mobile-first indexing. It means your website must be optimized for different mobile devices, ensuring a seamless experience for users regardless of the device they use to browse.
- XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt: XML sitemaps are roadmaps for search engine crawlers detailing your site’s vital pages. The robots.txt file, on the other hand, instructs search engine bots as to which pages to crawl and which to avoid. Search engines will focus on your most significant material when these files are configured correctly.
- On-Page SEO and Internal Linking: Each web page is optimized with relevant keywords, meta descriptions, alt texts, and header tags as part of the on-page SEO. Internal linking is adding links that will redirect visitors to a different web page of the same website. It makes navigation easier for the visitor and assists search engines in determining the structure of your site. Hence increasing the chances of ranking higher.
- External Factors & Backlinks: Backlinks from trustworthy websites work as testimonials for your content and website’s offerings. Backlinking on high-authority websites increases your website’s authority and encourages search engines to see your pages as significant resources, increasing the chances of ranking higher.
How to find and check crawlability and Indexability Issues?

The first step towards resolving issues is identification. The same applies to indexability and crawlability issues. Resolving crawlability and indexability issues is vital to ensure that search engines discover and index the website’s content. It is only then it will show to the searchers. Following are a few ways to find them!
- Robots.txt File: Verify that your website’s robots.txt file is not preventing search engine crawlers from accessing essential pages. Make certain that no important content is prohibited.
- XML Sitemap: Make an XML sitemap and submit it to search engines. It assists them in comprehending the structure of your website and the pages you want indexed. Update and examine the sitemap on a regular basis for accuracy.
- Google Search Console (GSC): Use GSC to uncover crawl mistakes, coverage issues, and indexation concerns. GSC gives valuable information on how Googlebot interacts with your website.
- Crawl Budget: Monitor your website’s crawl budget – the number of pages search engines crawl on your site each day. Ensure that important pages receive a sufficient crawl budget while low-value pages are minimized.
- Site Speed: Slow-loading pages can have an influence on crawlability SEO. Using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, examine and optimize the speed of your website on a regular basis.
- Internal Linking: Use correct internal linking to guarantee that all critical sites are linked together. It allows search engine crawlers to discover and index material successfully.
- HTTP Status Codes: Verify the correct HTTP status codes. Indexation can be hampered by pages that return 404 errors or other non-200 status codes. Use tools to discover and correct these problems.
- Duplicate Content: Duplicate content might be confusing to search engines and cause indexation issues. Make use of canonical tags to ensure that your preferred version of a page is correctly identified.
- Mobile Compatibility: Make sure your website is mobile-friendly. Mobile usability is a ranking criterion, and pages that are not mobile-friendly may not be efficiently indexed.
- Broken Links: Regularly sort out the broken internal and external links. They can disrupt the crawling process.
- Quality Content: Ensure to add high-quality, original content that is more likely to be indexed. Strictly avoid duplicate or low-value content that might not provide much value to users.
- User Experience: Great user experience encourages better crawlability. Clear navigation and user-friendly design help search engine crawlers navigate your site.
How to Optimize Crawlability and Indexability?
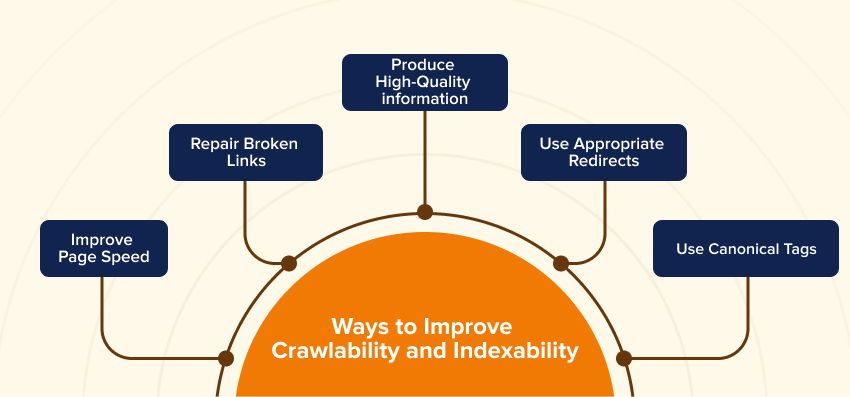
- Improve Page Speed: Slow-loading pages can turn off both search engine bots and users. Compress pictures, simplify code, and employ browser caching to enhance your site’s loading time.
- Repair Broken Links: Broken internal and external links can cause crawling to fail. To ensure a seamless experience, evaluate and update your connections regularly.
- Produce High-Quality information: Concentrate on producing unique, meaningful, and relevant information that solves the needs and questions of users.
- Use Appropriate Redirects: If you’ve relocated or deleted pages, use 301 redirects to lead users and search engines to the correct information.
- Use Canonical Tags: Use canonical tags to identify the preferred version for indexing when you have comparable content on many pages.
Tools for Optimizing Crawlability & Indexability
Following are some tools that will help you optimize your website’s crawlability & indexability.
- Google Search Console: This free Google tool gives information on how Googlebot perceives your website. It notifies you of indexing problems and lets you submit sitemaps.
- Screaming Frog: This desktop tool analyzes your website’s links, photos, and other resources to assist you in identifying crawlability problems.
- Yoast SEO: A well-known WordPress plugin that aids in on-page SEO, internal linking, and the generation of XML sitemaps.
- SEMrush: An all-in-one SEO tool that allows you to track crawlability and indexability progress over time.
Conclusion
Crawlability and indexability are critical components of effective SEO. Your website needs good crawlability and indexability for search engines to present your information to people, much as a library has an orderly catalog to assist readers in finding books. By ensuring that your site is easily crawlable, indexable, and optimized for both users and search engines, you are laying the groundwork for increased visibility and ranking. Accept these ideas and go on a path to make your internet presence truly discoverable!

FAQs
Crawlability is the search engine’s ability to scan and read the content of the website pages. SEO is the process of increasing web page crawlability and making it easier for the search engine to index the website. Else, it won’t appear in the search results. It will lead to poor website visibility and loss of business.
Use tools like Google Search Console’s “URL Inspection” to see if specific pages are indexed, or if a website is crawlable. The Robots.txt Tester determines whether specific pages are prevented from crawling. A basic Google search of “site:yourwebsite.com” yields indexed pages.
Crawling is a search engine’s process to scan web pages. Search engines release bots or crawlers to read and navigate the web pages to understand their content and identify the keywords. It then indexes the web pages and retrieves and shows them on the relevant searches.
Crawlability has a direct impact on indexation. If a site isn’t crawlable, search engines won’t be able to find and index its material. Crawlability ensures that a website’s pages are successfully crawled, resulting in effective indexation and a higher likelihood of appearing in search results.
An XML sitemap lists all the main pages on a website and assists search engines in understanding its structure. A robots.txt file, on the other hand, tells search engine bots which sites or areas they should not crawl. Crawlers are guided to key information via XML sitemaps, while robots.txt regulates access, contributing to a site’s crawlability and indexability by guiding the crawling process.







